China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News – this headline immediately grabs your attention, doesn’t it? This article dives deep into China’s incredible manufacturing dominance, exploring its historical rise, current capabilities, and the global implications. We’ll examine key industries, the complexities of global supply chains, and the challenges and future prospects for this economic giant. Get ready for a fascinating look at how China became—and remains—a manufacturing powerhouse.
We’ll trace China’s journey from its early manufacturing beginnings to its current position as a global leader. We’ll uncover the factors that fueled this growth, comparing its strengths and weaknesses against other major economies. We’ll also analyze the impact of automation, technological advancements, and geopolitical factors on China’s manufacturing dominance, considering both the opportunities and the risks involved for businesses and consumers worldwide.
China’s Manufacturing Superpower: China Is The Manufacturing Superpower | Hacker News

China’s meteoric rise as the world’s manufacturing hub is a complex story interwoven with economic reforms, global integration, and technological advancements. This article explores the historical context of this dominance, examining key industries, global supply chain dependencies, and future challenges and opportunities.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance: Historical Context
China’s transformation from an agrarian economy to a manufacturing giant is a remarkable feat spanning several decades. This evolution involved a series of strategic policy decisions, significant investments in infrastructure, and the leveraging of a vast and relatively low-cost workforce.
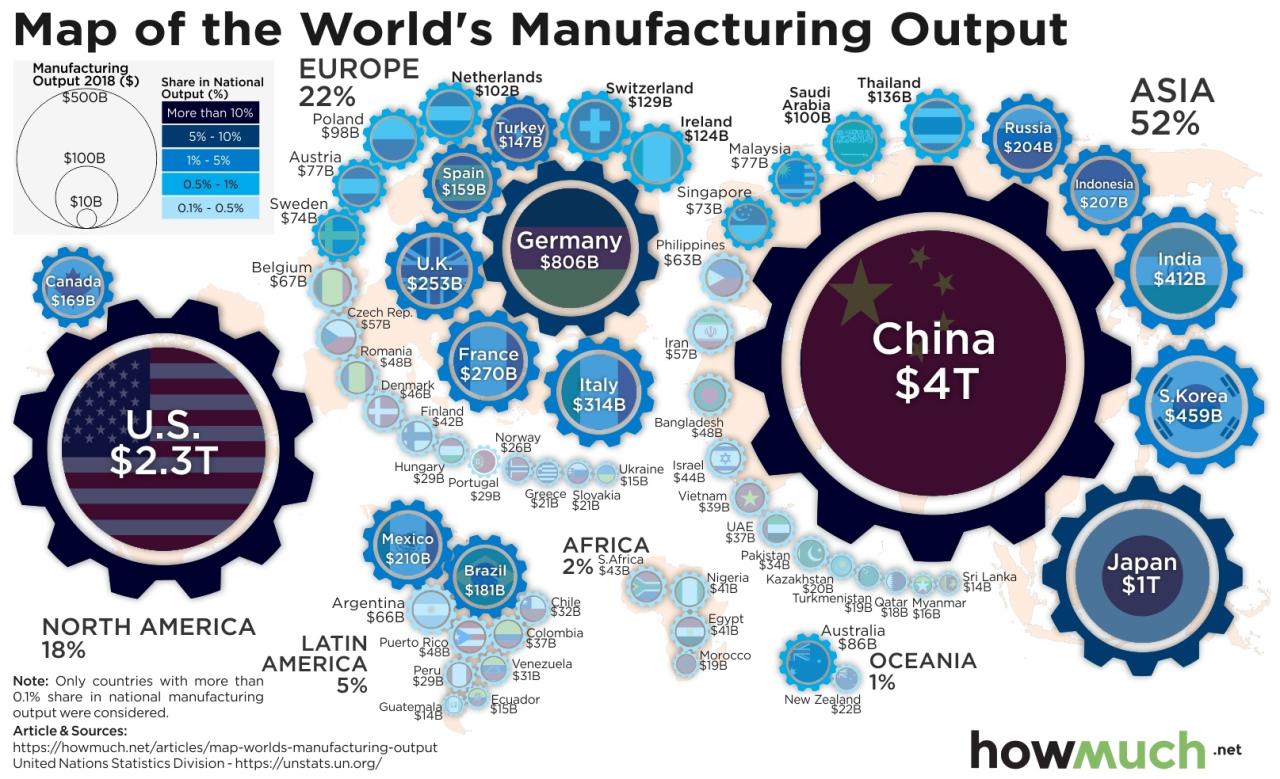
Key factors driving this rise include the implementation of economic reforms starting in 1978, the establishment of Special Economic Zones attracting foreign investment, and the country’s integration into the global trading system. While other economies like the US and Japan have strong manufacturing sectors, China’s scale and scope are unmatched, offering a vast array of products at competitive prices.
Compared to other major economies, China’s manufacturing sector boasts unparalleled production capacity, particularly in labor-intensive industries. While countries like Germany excel in high-precision engineering and the US in aerospace and defense, China’s strength lies in its ability to produce a wide range of goods at scale, efficiently, and cost-effectively.
| Date | Event | Impact | Supporting Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1978 | Economic Reforms Begin | Initiated market-oriented reforms, opening the door for foreign investment and private enterprise. | GDP growth accelerated significantly after 1978. |
| 1980s | Establishment of Special Economic Zones (SEZs) | Attracted substantial foreign direct investment (FDI) and spurred export-oriented manufacturing. | SEZs became major centers for export-oriented manufacturing, attracting global companies. |
| 2001 | Accession to the World Trade Organization (WTO) | Further integrated China into the global trading system, leading to increased trade and investment. | Significant increase in China’s export volume after WTO accession. |
| 2010s | Rise of E-commerce and Digital Manufacturing | Enabled faster production cycles, improved supply chain efficiency, and fostered innovation. | Rapid growth of e-commerce platforms like Alibaba and JD.com, supporting online manufacturing. |
Key Industries and Production Capabilities
China’s manufacturing prowess is evident across diverse sectors. Its leading industries leverage technological advancements to enhance productivity and quality.
- Electronics: China is the world’s largest producer of electronics, encompassing smartphones, computers, and consumer electronics. Technological advancements in automation and precision engineering are driving this sector.
- Textiles: China remains a major player in the textile industry, benefiting from its extensive supply chains and cost-effective production processes. Innovations in textile technology continue to enhance efficiency and product quality.
- Automobiles: With both domestic and international brands operating in China, the automotive industry is a significant contributor to the nation’s manufacturing output. Advancements in electric vehicle (EV) technology are shaping the future of this sector.
- Renewable Energy: China is a global leader in the manufacturing of solar panels and wind turbines, driven by government support and technological advancements in renewable energy technologies.
Generally, Chinese-made goods offer a compelling balance of quality and cost-effectiveness, particularly in high-volume production. While quality can vary across industries and manufacturers, continuous improvements are observed as Chinese companies invest in technology and quality control measures.
Global Supply Chains and Dependence on China, China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News

Global supply chains are heavily reliant on China’s manufacturing capabilities. This dependence presents both opportunities and risks for businesses and consumers worldwide.
The implications of this reliance are significant. Businesses benefit from access to a vast and efficient manufacturing base, while consumers enjoy lower prices for a wide range of goods. However, over-reliance on a single manufacturing powerhouse creates vulnerabilities.
Potential risks include geopolitical instability, disruptions to production due to natural disasters or pandemics, and the potential for trade disputes. A hypothetical scenario: A major disruption to Chinese manufacturing, such as a prolonged pandemic or a significant geopolitical event, could trigger global shortages, price hikes, and significant economic instability across numerous sectors.
Challenges and Future Prospects for Chinese Manufacturing

China’s manufacturing sector faces several challenges, including rising labor costs, environmental concerns, and the need for technological upgrades.
The Chinese government is actively addressing these challenges through policies promoting technological innovation, sustainable manufacturing practices, and investment in higher-skilled labor. Predictions regarding the future trajectory of Chinese manufacturing dominance suggest a continued strong presence, albeit with a shift towards higher-value-added manufacturing and greater automation.
Future technological disruptions could include advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and 3D printing, which will reshape manufacturing processes and potentially alter the competitive landscape.
The long-term outlook for Chinese manufacturing is one of continued growth, but with a greater emphasis on technological sophistication, sustainability, and resilience to global shocks.
The Role of Technology and Automation
Automation and technological advancements are reshaping China’s manufacturing landscape, improving efficiency and productivity.
So you’re reading about China’s manufacturing dominance on Hacker News? Take a quick break from all that global economics and check out the amazing Quadrantid meteor shower – find out when and how to best see it by checking out this guide: Quadrantid meteor shower to light up skies – here’s the best way to. Then, get back to pondering how China’s factories power so much of the world.
China’s adoption of automation technologies is accelerating, although it still lags behind some advanced economies in certain areas. The impact on employment is complex, with some jobs being displaced by automation, while new opportunities emerge in areas such as robotics maintenance and software development.
For example, the use of industrial robots in electronics assembly has increased significantly, boosting productivity and improving product quality. Similarly, AI-powered quality control systems are enhancing precision and reducing defects.
Geopolitical Implications of China’s Manufacturing Power
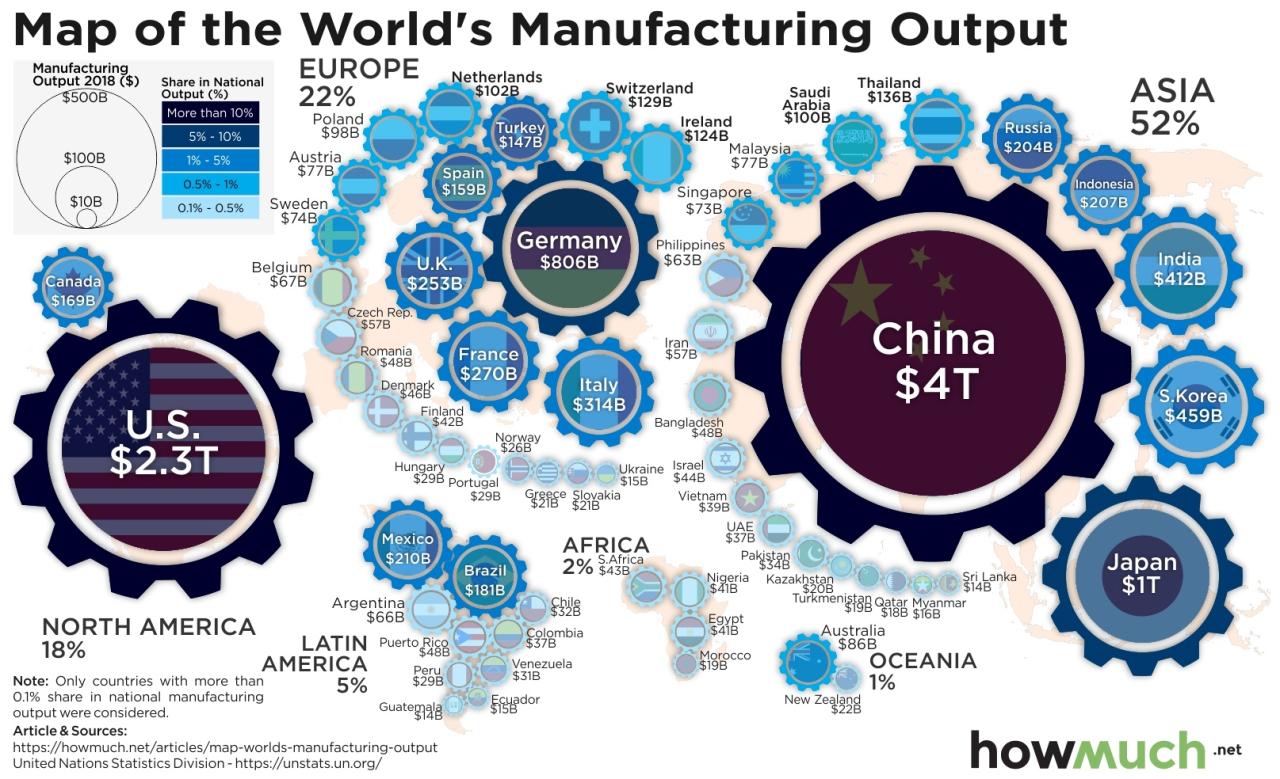
China’s manufacturing dominance has significant geopolitical implications, influencing international trade, economic relations, and global power dynamics.
Other countries are employing various strategies to compete with China, including investing in domestic manufacturing, fostering technological innovation, and diversifying supply chains. The potential for trade wars and other economic conflicts remains a concern, as nations seek to balance their economic interests with geopolitical considerations.
| Country | Strength | Weakness | Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | Massive production capacity, cost-effective labor, complete supply chains | Rising labor costs, environmental concerns, technological dependence in some areas | Focus on technological innovation, high-value manufacturing, and sustainable development |
| United States | Strong technological base, advanced manufacturing capabilities in specific sectors | Higher labor costs, reliance on imports for certain goods | Reshoring initiatives, investment in advanced manufacturing technologies |
| Germany | High-precision engineering, strong industrial base, skilled workforce | Relatively high labor costs, dependence on exports | Focus on Industry 4.0, automation, and high-value manufacturing |
Ultimate Conclusion
China’s manufacturing superpower status is undeniable, but its future isn’t predetermined. While challenges like rising labor costs and environmental concerns exist, China’s continued investment in technology and automation positions it for continued success. The global economy remains deeply intertwined with China’s manufacturing capabilities, making understanding its trajectory crucial for businesses and policymakers alike. The story of China’s manufacturing dominance is far from over; it’s a dynamic and evolving narrative that continues to shape the global landscape.
Clarifying Questions
What are some examples of specific technologies transforming Chinese manufacturing?
AI-powered quality control, 3D printing for rapid prototyping, and advanced robotics for automation are just a few examples.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – a lot of those supply chains rely on robust software. If you’re a full-stack developer looking to capitalize on this, check out the freelance opportunities and rates here: full stack developer freelance opportunities and rates. The demand for skilled developers in this area is huge, mirroring China’s massive manufacturing output.
How is China addressing environmental concerns in its manufacturing sector?
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – a lot of those products probably use AI-generated voiceovers in their marketing! If you’re curious about the tech behind that, check out this helpful guide on comparing different AI voice generator software options. Understanding the AI side of things helps paint a fuller picture of China’s global manufacturing influence, right?
China is investing heavily in renewable energy, implementing stricter environmental regulations, and promoting green manufacturing practices.
What are the biggest risks associated with over-reliance on Chinese manufacturing?
Geopolitical instability, supply chain disruptions, and potential trade wars are significant risks.
How does China’s manufacturing dominance affect consumers?
It generally leads to lower prices for many goods, but also raises concerns about quality control and ethical labor practices.