How to operate a drone? It’s a question many ask, intrigued by the possibilities of aerial exploration and captivating imagery. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from pre-flight checklists and safety procedures to mastering advanced flight techniques and adhering to legal regulations. Whether you’re a novice eager to take flight or an experienced pilot looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive resource provides the knowledge and practical steps needed for safe and successful drone operation.
We’ll cover everything from understanding basic controls and navigating various flight modes to capturing stunning aerial photos and videos. Learn about essential maintenance practices, legal compliance, and emergency procedures to ensure a smooth and enjoyable drone experience. We’ll even explore advanced techniques like waypoint missions and cinematic shot creation, unlocking the full potential of your drone.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Prior to any drone operation, a thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring safe and successful flights. This involves assessing various factors that can impact flight stability and safety, from battery levels to weather conditions.
Pre-flight Checklist, How to operate a drone
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist should include the following steps:
- Battery Level Check: Ensure the drone battery is sufficiently charged. A low battery can lead to an unexpected power failure mid-flight.
- GPS Signal Strength: Verify a strong GPS signal is acquired. A weak signal can result in inaccurate positioning and potential loss of control.
- Propeller Inspection: Check the propellers for any damage or debris. Damaged propellers can cause instability or failure during flight.
- Weather Conditions: Assess wind speed, precipitation, and visibility. High winds, heavy rain, or low visibility can create hazardous flying conditions.
- Calibration: Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) to ensure accurate readings.
- Flight Area Inspection: Survey the flight area for any obstacles, people, or airspace restrictions.
- Emergency Procedures Review: Briefly review emergency procedures, including low-battery protocols and loss-of-signal responses.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Sequence

A smooth and controlled takeoff and landing is vital for preventing accidents. Follow these steps:
- Power Up: Power on the drone controller first, followed by the drone itself.
- GPS Acquisition: Allow the drone sufficient time to acquire a stable GPS signal before takeoff.
- Takeoff: Initiate takeoff slowly and steadily, maintaining visual contact with the drone at all times.
- Flight Operations: Execute your planned flight operations.
- Landing Approach: Begin the landing approach by slowly descending to a suitable altitude.
- Landing: Gently lower the drone to the ground, ensuring a smooth and controlled landing.
- Power Down: Power down the drone first, followed by the controller.
Drone Battery Comparison
| Battery Type | Capacity (mAh) | Flight Time (minutes) | Weight (grams) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo 3S 1500mAh | 1500 | 15-20 | 150 |
| LiPo 4S 2200mAh | 2200 | 25-30 | 200 |
| LiHV 4S 2200mAh | 2200 | 30-35 | 200 |
| LiPo 6S 3000mAh | 3000 | 35-40 | 250 |
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Effective drone operation relies on understanding the controller and mastering basic flight controls. This section details how to manage these aspects for safe and precise flights.
Drone Controllers and Functionalities
Drone controllers vary in design and features, but generally include joysticks for controlling movement, buttons for various functions (camera, return-to-home, etc.), and a screen for displaying telemetry data. Some advanced controllers offer customizable settings and integrated GPS navigation.
Basic Flight Controls
The four fundamental flight controls are:
- Throttle: Controls altitude (up and down).
- Pitch: Controls forward and backward movement.
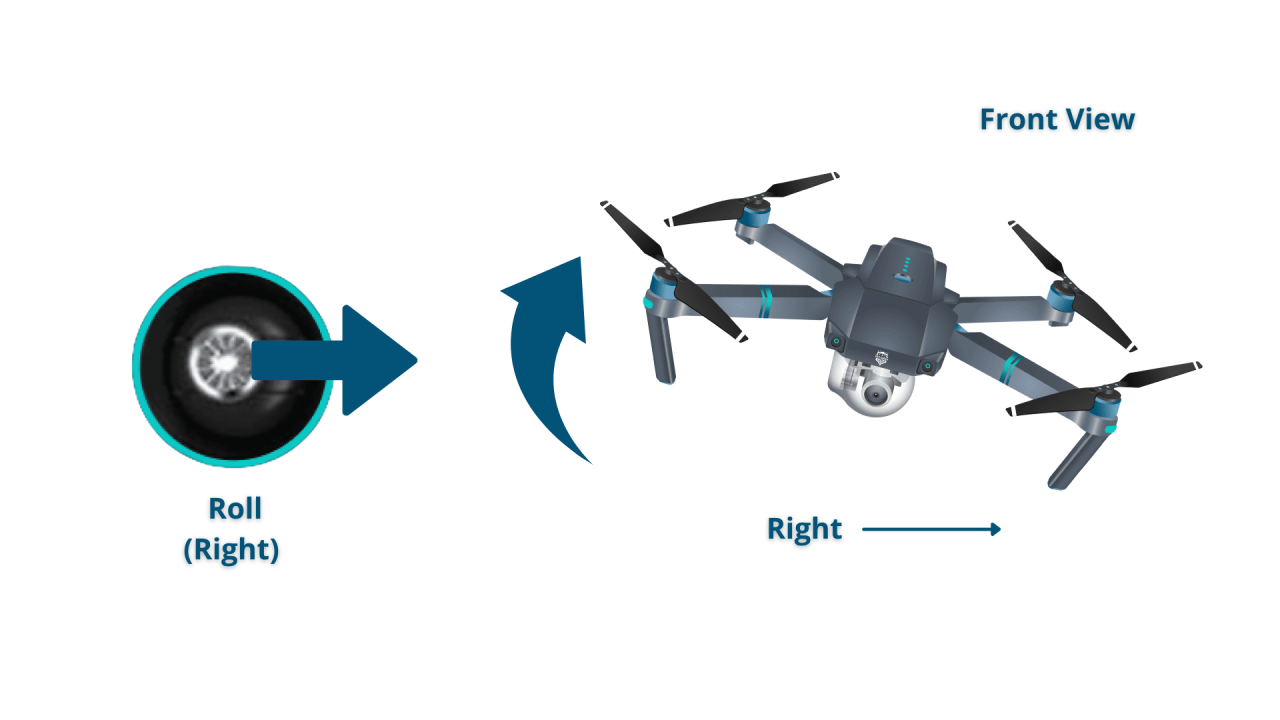
- Roll: Controls left and right movement.
- Yaw: Controls rotation around the vertical axis (left and right turns).
Maintaining Stable Control in Wind
Wind can significantly impact drone stability. To maintain control in windy conditions:
- Fly into the wind: This provides a more stable platform for takeoff and landing.
- Use smaller, smoother control inputs: Avoid jerky movements that can exacerbate the effects of wind.
- Reduce speed and altitude: Flying lower and slower reduces the impact of wind gusts.
- Consider wind mitigation techniques: Using advanced features like wind compensation can help stabilize the drone.
GPS Coordinate Navigation
Precise navigation using GPS coordinates involves inputting specific latitude and longitude values into the drone’s flight controller. This allows for automated flight to pre-determined locations, facilitating accurate data acquisition for various applications.
- Identify Target Coordinates: Obtain the latitude and longitude coordinates of your target location.
- Input Coordinates: Enter the coordinates into your drone’s flight controller software.
- Initiate Flight: Command the drone to fly to the specified coordinates.
- Monitor Flight: Observe the drone’s progress and make adjustments as needed.
- Reach Destination: The drone will automatically navigate to the entered coordinates.
Flight Modes and Features
Modern drones offer various flight modes and automated features designed to enhance safety and ease of operation. Understanding these features is crucial for efficient and safe drone operation.
Flight Mode Comparison
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and flight scenarios:
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness, ideal for beginners.
- Sport Mode: Offers increased speed and responsiveness for more experienced pilots.
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS for positioning and stability, enhancing precision.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains drone orientation relative to the pilot, irrespective of GPS signal.
Automated Features: Return-to-Home (RTH)
RTH automatically returns the drone to its home point, typically its takeoff location. This is a crucial safety feature in case of signal loss or low battery. While convenient, relying solely on RTH without maintaining visual contact can be risky in complex environments.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully piloting a drone requires careful attention to safety regulations and proper handling of the equipment. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and enhance your skills.
Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation comes with practice and a solid understanding of the fundamentals.
Activating and Utilizing Drone Features
Activating features like obstacle avoidance typically involves selecting the appropriate mode or setting within the drone’s control interface. These features enhance safety but should not be relied upon completely, as they may not detect all obstacles.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Addressing malfunctions promptly is crucial for preventing accidents and damage. Here are some common issues and troubleshooting steps:
- Low Battery: Initiate RTH immediately, or carefully land the drone.
- Loss of Signal: The drone may enter RTH mode automatically. If not, try regaining signal or initiate a manual landing.
- GPS Failure: Land the drone immediately. GPS failure can lead to inaccurate positioning.
- Propeller Failure: Land the drone immediately. A damaged propeller can cause instability and crashes.
- Gimbal Malfunction: Check gimbal settings and power cycle the drone. If the problem persists, consider professional repair.
Aerial Photography and Videography Techniques
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings, flight techniques, and post-processing. This section provides guidance on achieving professional-looking results.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Photos
- Choose the right time of day: The “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) provides soft, even lighting.
- Set the correct camera settings: Adjust ISO, aperture, and shutter speed based on lighting conditions.
- Maintain a stable flight: Avoid jerky movements that can lead to blurry images.
- Compose your shots carefully: Consider the rule of thirds and other composition techniques.
- Use the drone’s camera features: Explore features like HDR and exposure bracketing.
Achieving Stable Shots
Stable shots are crucial for professional-looking results. Techniques include:
- Flying smoothly: Avoid sudden movements.
- Using gimbal stabilization: Most drones have a three-axis gimbal to minimize camera shake.
- Flying in calm conditions: Wind can significantly affect image stability.
- Post-processing stabilization: Software can help stabilize shaky footage.
Planning and Executing Complex Aerial Shots
Planning is essential for complex shots like circling and tracking subjects. Use waypoints or manual control with precision and practice.
Setting Up and Adjusting Drone Camera Settings
Optimal image quality depends on proper camera settings. Experiment with different settings to find the best balance for your specific conditions and desired aesthetic.
Drone Maintenance and Storage
Regular maintenance and proper storage are vital for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued safe operation. This section details procedures for cleaning, maintaining, and storing your drone.
Cleaning and Maintaining Drone Components
Regular cleaning of propellers, camera lenses, and other components is crucial. Use appropriate cleaning tools and avoid harsh chemicals.
Proper Battery Storage and Charging
Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from flammable materials. Charge batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions, avoiding overcharging or deep discharging.
Regular Drone Maintenance and Inspection Schedule
Establish a regular maintenance schedule, including visual inspections for damage, battery checks, and firmware updates.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, from pre-flight checks to mastering altitude and direction, is crucial. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical tips and troubleshooting, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering these skills ensures safe and effective drone operation.
Safe Drone Storage
Store the drone in a protective case or container, away from moisture and extreme temperatures. Proper storage prevents damage and extends its lifespan.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Understanding and adhering to local drone regulations is paramount. This section highlights the importance of legal compliance and Artikels key procedures.
Understanding Local Drone Regulations
Familiarize yourself with all applicable local, state, and national regulations regarding drone operation. These regulations vary by location and can include airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and operational limitations.
Restricted and Prohibited Flight Areas
Many areas are restricted or prohibited for drone flight, including airports, military bases, and sensitive infrastructure. Always check airspace maps before flying.
Drone Registration Procedures
In many jurisdictions, drone registration is mandatory. Follow the specific procedures Artikeld by the relevant authorities to register your drone.
Implications of Violating Drone Regulations
Violating drone regulations can result in fines, confiscation of the drone, and even criminal charges. Always prioritize safe and legal drone operation.
Emergency Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
Being prepared for emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation. This section Artikels procedures for handling various emergency scenarios.
Steps to Take in Case of Drone Malfunction
In the event of a malfunction, prioritize safety. If possible, initiate RTH. If not, attempt a controlled landing. If the drone is uncontrollable, allow it to land safely and assess the damage.
Handling Emergency Situations
Emergency situations such as low battery or loss of signal require swift action. Initiate RTH immediately, or attempt a controlled landing.
Retrieving a Crashed Drone
When retrieving a crashed drone, prioritize your safety. Assess the situation, and if necessary, seek assistance from others.
Emergency Checklist
- Assess the situation.
- Initiate RTH or attempt a controlled landing.
- If the drone is uncontrollable, allow it to land safely.
- Check for damage.
- Report the incident to relevant authorities if necessary.
Advanced Drone Techniques

Beyond basic operation, advanced techniques unlock greater capabilities for aerial photography, videography, and professional applications.
Waypoint Missions
Waypoint missions allow for automated flights along predefined paths, facilitating complex shots and data acquisition.
Achieving Cinematic Aerial Shots
Cinematic shots involve smooth, deliberate movements and creative camera angles. Practice and experimentation are key.
Drone Software for Post-Processing
Software like Adobe Premiere Pro and DaVinci Resolve allow for advanced editing and color grading of aerial footage.
Professional Drone Applications
Drones find applications in various professional fields, including inspection, surveying, and agriculture. Specialized skills and training are often required.
Illustrative Example: Drone Inspection of a Bridge
Imagine a scenario where a drone is used to inspect a bridge for structural damage. This example illustrates the process from pre-flight preparation to post-flight analysis.
Drone Inspection Process
The inspection would begin with a thorough pre-flight checklist, including a careful assessment of weather conditions and a review of the bridge’s structural features to plan the flight path. A detailed flight plan would be developed, outlining the necessary camera angles and altitudes for capturing comprehensive imagery of the bridge’s various components, including the deck, supports, and abutments. The drone would then be flown systematically along this pre-planned route, capturing high-resolution photos and videos.
After the flight, the data would be downloaded and processed using specialized software to enhance the images and videos. Experienced engineers would then analyze the imagery to identify potential cracks, corrosion, or other signs of structural damage. The analysis might reveal areas needing immediate attention, such as significant cracking in the support pillars or signs of corrosion on the bridge’s metal components.
Images might show subtle variations in color or texture that indicate areas of stress or damage. Detailed reports, complete with annotated images and videos, would then be generated, providing crucial information for bridge maintenance and repair decisions. The visual data acquired via the drone provides a cost-effective and efficient way to assess the bridge’s condition compared to traditional inspection methods.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technical skill with a keen understanding of safety and regulations. This guide has equipped you with the fundamental knowledge and practical steps to confidently navigate the skies. Remember that consistent practice, adherence to safety protocols, and continuous learning are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot.
Embrace the thrill of flight, capture breathtaking moments, and explore the world from a unique perspective – all while adhering to responsible flight practices.
Detailed FAQs
What is the best drone for beginners?
Several user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, prioritizing ease of use and safety features. Research models known for their stability and intuitive controls.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration is crucial for accurate flight. Perform this before each flight session, especially if operating near magnetic interference.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a Return-to-Home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If RTH fails, visually locate your drone and attempt a manual landing.
Can I fly my drone in rain or snow?
No. Operating a drone in adverse weather conditions is dangerous and can damage the aircraft. Always check weather forecasts before flying.
